 [www.cellbiol.com/bioinformatics_web_development/chapter-1-internet-networks-and-tcp-ip/the-tcpip-family-of-internet-protocols/]
[www.cellbiol.com/bioinformatics_web_development/chapter-1-internet-networks-and-tcp-ip/the-tcpip-family-of-internet-protocols/]3.1.1 Identify different types of networks.
Examples include local area network (LAN), virtual local area network (VLAN), wide area network (WAN), storage area network (SAN), wireless local area network (WLAN), internet, extranet, virtual private network (VPN), personal area network (PAN), peer-to-peer (P2P).
INT Globalization has been accelerated by the technical advances linked to network development.
3.1.2 Outline the importance of standards in the construction of networks.
INT Standards enable compatibility through a common "language" internationally.
3.1.3 Describe how communication over networks is broken down into different layers.
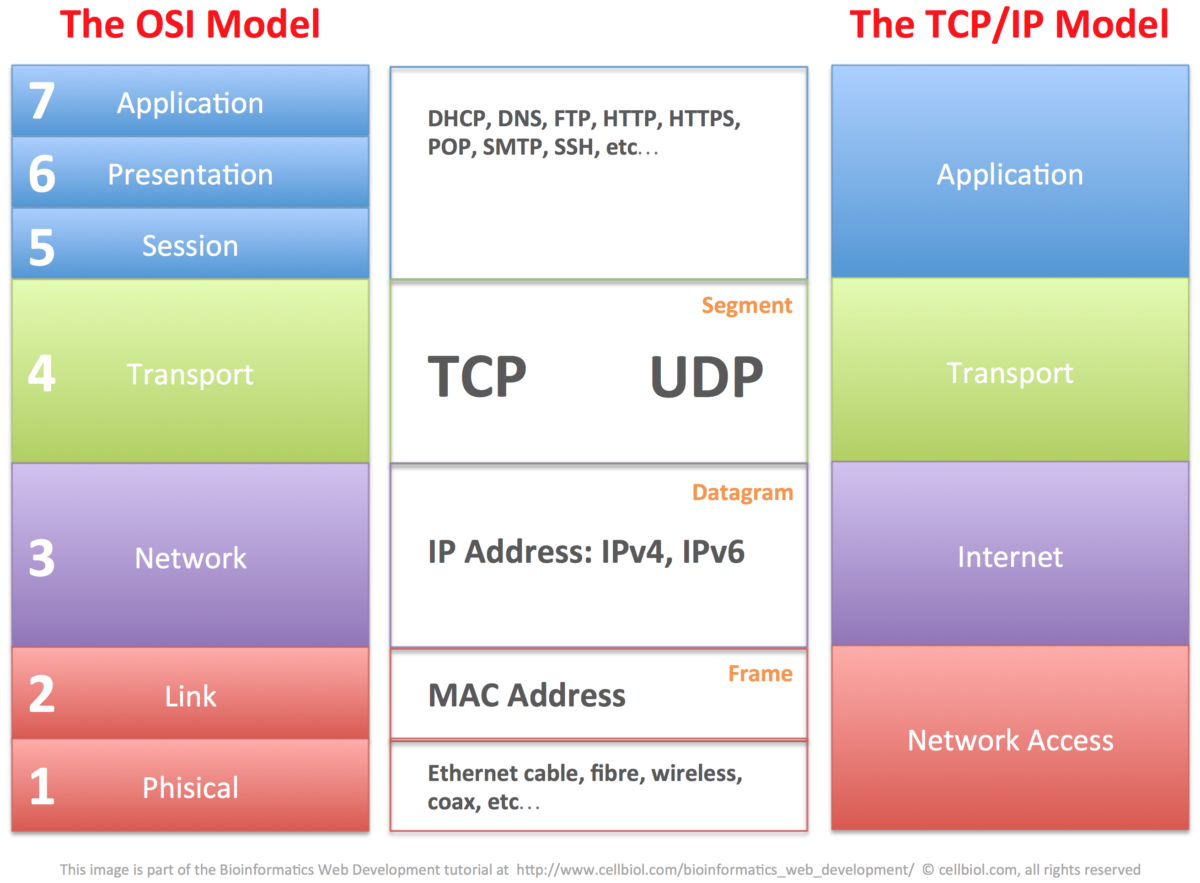
Awareness of the OSI seven layer model is required, but an understanding of the functioning of each layer is not. An overview is given below but not all implementations follow the OSI model for example a four layer model is more accurate for TCP/IP (Application, Transport, Internet, Network)
| Layer name | What might happen in that layer | |
| 7 | Application | Application software |
| 6 | Presentation | Data formatting / Encryption/Decryption |
| 5 | Session | Manage connections being used (sockets); starts and stops client/server connections |
| 4 | Transport | Packet preparation and ordering; Transmission error detection (TCP) or not (UDP) |
| 3 | Network | Routing (IP) |
| 2 | Data | Network Interface Card; Conversion to physical signal |
| 1 | Physical | Cabling or wireless transmitters/ receivers |
 [www.cellbiol.com/bioinformatics_web_development/chapter-1-internet-networks-and-tcp-ip/the-tcpip-family-of-internet-protocols/]
[www.cellbiol.com/bioinformatics_web_development/chapter-1-internet-networks-and-tcp-ip/the-tcpip-family-of-internet-protocols/]
3.1.4 Identify the technologies required to provide a VPN.
3.1.5 Evaluate the use of a VPN. 3 S/E, AIM 9 The use of a VPN has led to changes in working patterns.
3.1.6 Define the terms: protocol, data
packet.
3.1.7 Explain why protocols are necessary
Including data integrity, flow control, deadlock, congestion, error checking.
johnrayworth 3.1.7 notes3.1.8 Explain why the speed of data transmission across a network can vary.
3.1.9 Explain why compression of data is often necessary when transmitting across a network.
INT Compression has enabled information to be disseminated more rapidly.
3.1.10 Outline the characteristics of different transmission media.
Characteristics include: speed, reliability, cost and security. Transmission media include: metal conductor, fibre optic, wireless.
3.1.11 Explain how data is transmitted by packet switching.
3.1.12 Outline the advantages and disadvantages of wireless networks.
S/E wireless networks have led to changes in working patterns, social activities and raised health issues.
3.1.13 Describe the hardware and software components of a wireless network.
3.1.14 Describe the characteristics of wireless networks.
Include: WiFi; Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX); 3G mobile; future networks.
WiMax provides a wireless link that can be used to provide broadband wireless access direct to devices without the necessity to go through a WLAN. More information.
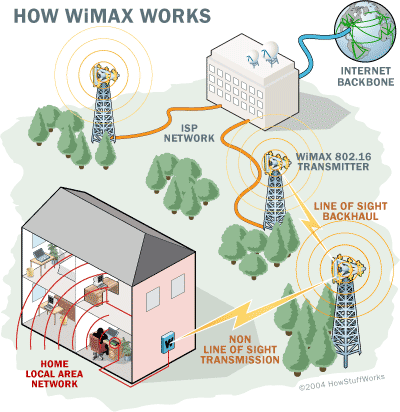
S/E, INT Connectivity between different locations.
WiMAX, an IEEE standard (802.16) is now known primarily as a last mile, fixed wireless access technology to be used for internet access where it competes with cable and DSL. Its data rates typically max out at 30 to 40 Mb/s. However, recent upgrades to the standard now provide data rates to 1 Gb/s. WiMAX is still available, but mostly outside the U.S. It "lost" the battle with LTE.
electronicdesign.com3.1.15 Describe the different methods of network security.
Include encryption types, userID, trusted media access control (MAC) addresses.
S/E Wireless networks have led to concerns about the security of the user's data.
3.1.16 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each method of network security.